9. HTTP Headers
HTTP Headers
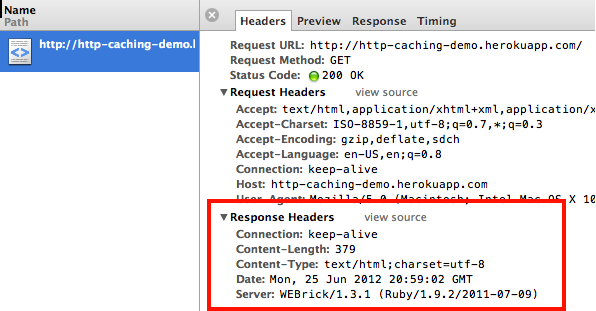
HTTP headers let the client and the server pass additional information with an HTTP request or response. An HTTP header consists of its case-insensitive name followed by a colon (:), then by its value. Whitespace before the value is ignored.
There are numerous types of HEADERS in HTTP. Some can be used for both requests and responses and others are specific to the message types.
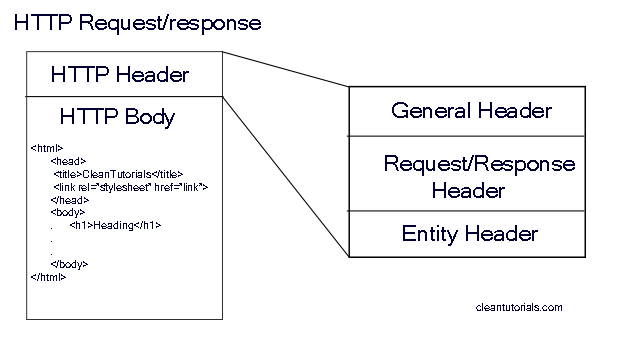
There are four kinds of headers context-wise:
- General headers apply to both requests and responses, but with no relation to the data transmitted in the body.
- Request headers contain more information about the resource to be fetched, or about the client requesting the resource.
- Response headers hold additional information about the response, like its location or about the server providing it.
- Entity headers contain information about the body of the resource, like its content length or MIME type.
Some common header types:
General Headers
- Connection - tells the other end whether connection should close after HTTP transmission
- Content-Encoding - specifies the type of encoding
- Content-Length - specifies the content length
- Content-Type - specifies the content type
- Transfer-Encoding - specifies the encoding on the message body
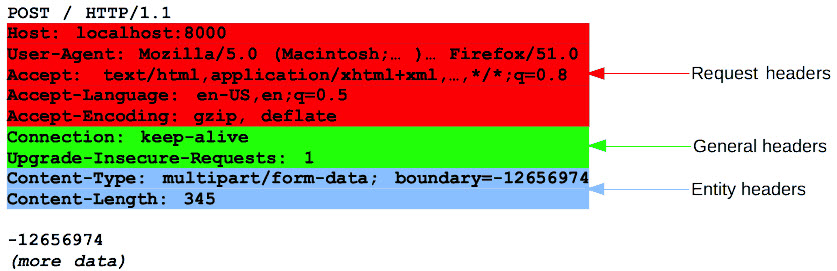
Request Headers
- Accept - specifies to the server what type of content it will accept
- Accept-Encoding - specifies to the server what type of message encoding it will accept
- Authorization - submits credentials
- Cookie - submits cookies to server
- Host - specifies host name
- If-Modified-Since - specifies WHEN browser last received the resource. If not modified, the server instructs the client to use cached copy
- If-None-Match - specifies entity tag
- Origin - specifies the domain where the request originated
- Referer - specifies the URL of the requestor
- User-Agent - specifies the browser that generated the request
Response Headers
- Access-Control-Allow-Origin - specifies whether the resource can be retrieved via cross-domain
- Cache-Control - passes caching directive to the browser
- Etag - specifies an entity tag (notifies the server of the version in cache)
- Expires - specifies how long the contents of the message body are valid
- Location - used in redirect responses (3xx)
- Pragma - passes caching directives to browser
- Server - specifies the web server software
- Set-Cookie - issues cookies
- WWW-Authenticate - provides details of type of authentication supported
- X-Frame-Options - whether and how response may be loaded within browser frame